Do you know? that global cybercrime damages surpassed $9.5 trillion, with eCommerce platforms like Shopify becoming prime targets. As digital commerce grows, so does the sophistication of cyber threats. Shopify store owners are now grappling with more than just sales and inventory, they face rising risks of data breaches, phishing, and malicious bot attacks.
For small to mid-sized businesses (SMBs), this translates into sleepless nights, compliance anxieties, and potential revenue loss. Traditional security tools often fall short or become costly add-ons.
Enter Shopify’s evolving suite of Shopify services, security tools, AI-driven threat detection, and robust compliance features designed for 2025 and beyond. This blog explores practical, cost-effective steps to fortify your store, ensuring that your customers’ data, and your brand reputation, remain secure. If you’re serious about scaling responsibly, protecting your Shopify store with the right services isn’t optional, it’s mission-critical.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding the Growing Cybersecurity Challenges in 2025
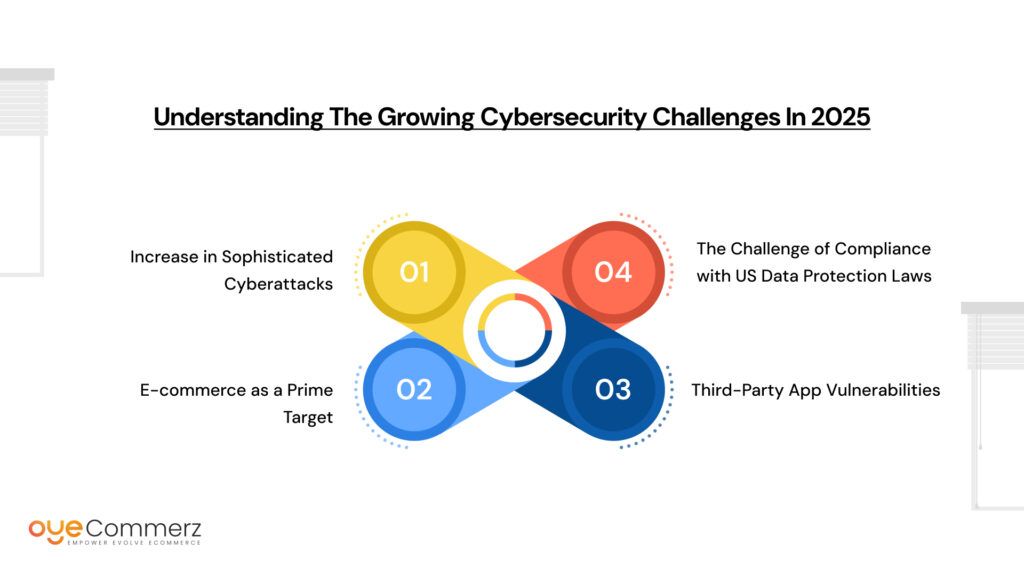
As e-commerce continues to grow, so do the risks. Cybercriminals are getting more advanced, making it crucial for store owners to stay ahead. If you’re running a Shopify store against emerging cyber threats, understanding the biggest security challenges in 2025 will help you build stronger defenses.
Increase in Sophisticated Cyberattacks
Cybercriminals are using AI-powered attacks, making them harder to detect. In 2025, we expect to see:
- Targeted phishing scams that mimic Shopify emails to steal login details.
- AI-driven malware that can bypass traditional security measures.
- Automated brute force attacks on Shopify admin panels.
E-commerce as a Prime Target
With billions of dollars flowing through online stores, Shopify merchants have become high-value targets. Hackers go after:
- Customer payment data for resale on the dark web.
- Store credentials to take control of Shopify accounts.
- Shopify checkout pages to inject fake payment forms.
Third-Party App Vulnerabilities
While apps enhance functionality, they can also introduce security risks. Some poorly developed apps may:
- Have weak security, allowing hackers to access customer data.
- Request excessive permissions, leading to data leaks.
- Lack updates, making them vulnerable to new exploits.
The Challenge of Compliance with US Data Protection Laws
As regulations tighten, Shopify store owners must comply with:
- CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) – Protecting customer data and requiring disclosure of data collection.
- PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) – Ensuring secure payment transactions.
- GDPR (if selling to EU customers) – Additional privacy requirements for international merchants.
Ignoring compliance can result in fines, lawsuits, and loss of customer trust.
Common Cybersecurity Threats Shopify Store Owners Face
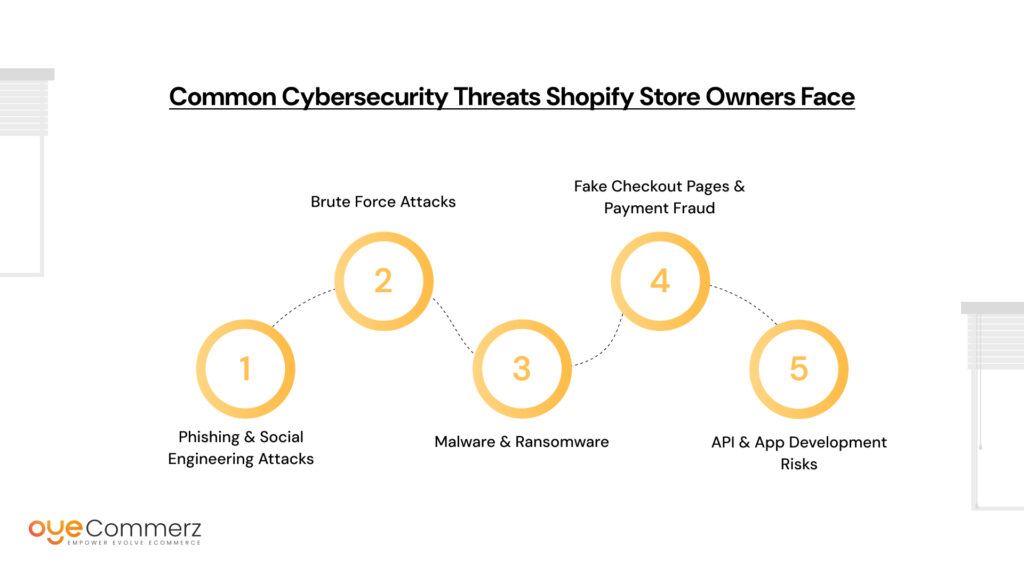
Running a Shopify store against emerging cyber threats requires awareness of the latest risks. Cybercriminals continuously develop new tactics to exploit vulnerabilities in e-commerce platforms, making security a top priority for store owners. Here are the most common threats Shopify merchants face in 2025.
Phishing & Social Engineering Attacks
Hackers often send fake emails pretending to be from Shopify, payment processors, or service providers. These emails trick store owners into revealing login credentials, payment information, or customer data. Attackers also use social engineering tactics, such as impersonating employees or support teams, to gain access to sensitive information.
Brute Force Attacks
Brute force attacks involve automated bots attempting thousands of password combinations to break into Shopify admin panels. Stores with weak or reused passwords are particularly vulnerable. Once hackers gain access, they can alter store settings, steal payment data, or redirect customer transactions.
Malware & Ransomware
Cybercriminals use malware to infect Shopify stores through malicious links, unsecured third-party apps, or compromised plugins. Ransomware is another growing threat, where hackers lock store owners out of their Shopify accounts and demand a ransom to regain access.
Fake Checkout Pages & Payment Fraud
Attackers create fake checkout pages that look identical to the real Shopify payment portal. Customers unknowingly enter their credit card details, which are then stolen and used for fraudulent transactions. Payment fraud, including chargeback scams and stolen credit card use, also remains a major concern for Shopify merchants.
API & App Development Risks
Many store owners rely on third-party apps for added functionality, but not all apps follow strict security standards. Poorly developed apps may:
- Expose store data due to weak encryption or unsecured connections.
- Request excessive permissions that compromise customer privacy.
- Become outdated, leaving security gaps that hackers can exploit.
Understanding these threats is the first step to protecting your Shopify business. In the next section, we will explore best practices to secure your Shopify store against emerging cyber threats and keep your store and customers safe.
How to Secure Your Shopify Store: Best Practices for 2025
Now that you understand the risks, it’s time to take action. Securing your Shopify store against emerging cyber threats requires a combination of basic security measures and advanced technical strategies. Whether you’re just starting or running a growing e-commerce business, these best practices will help safeguard your store.
Basic Security Measures (For New E-commerce Businesses)
Use Strong Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Create complex passwords with a mix of uppercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Enable 2FA for your Shopify admin to add an extra layer of protection.
Keep Shopify and Apps Updated
Regular updates fix security vulnerabilities and protect against new threats. Avoid using outdated apps that may expose your store to risks.
Limit User Access and Permissions
Assign specific roles and permissions to team members based on their tasks. Restrict access to sensitive data to prevent unauthorized modifications.
Advanced Security Steps (For Scaling Businesses and Tech-Savvy Owners)
Leverage Shopify’s Built-in Security Features
Shopify provides SSL encryption, fraud analysis, and automated updates to secure stores. Use Shopify Payments for transactions, as it includes advanced fraud protection.
Install Trusted Security Apps
Use apps that offer firewalls, malware detection, and bot protection. Choose apps with strong security protocols and regular updates.
Secure API Integrations and App Development
Only install third-party apps from the Shopify App Store to ensure security compliance. Regularly review app permissions and remove unused or outdated apps. If developing custom apps, follow secure coding practices to prevent data leaks.
Conduct Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Run security scans to identify vulnerabilities before hackers do. Perform penetration testing to simulate cyberattacks and strengthen defenses.
By implementing these security measures, you can protect your Shopify store against emerging cyber threats and ensure the safety of your business and customers.
Comparison Table: Shopify Security vs. Other E-commerce Platforms
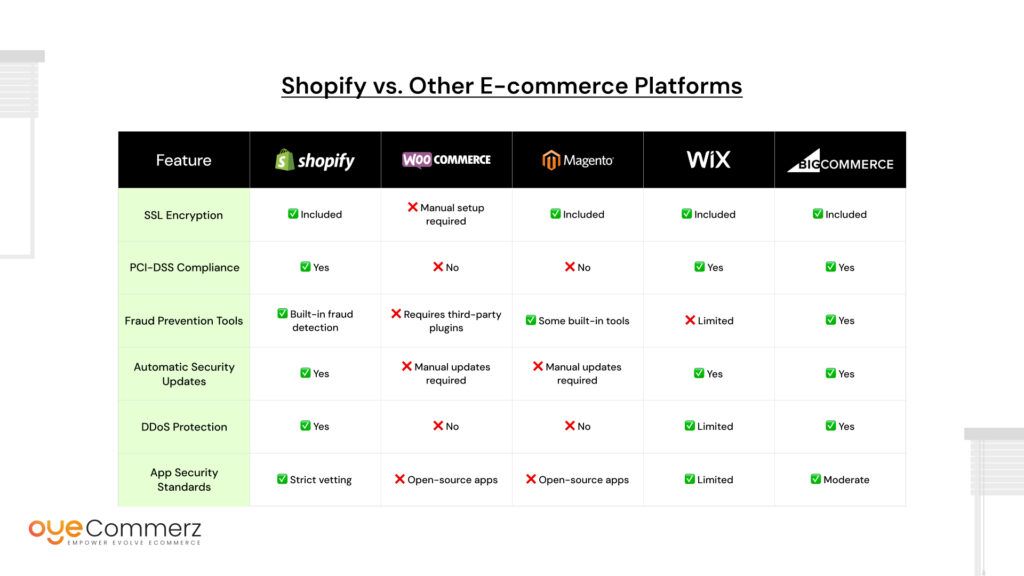
When choosing an e-commerce platform, security should be a top priority. A Shopify store against emerging cyber threats offers built-in protections that many other platforms lack. Below is a comparison of Shopify’s security features against other popular e-commerce platforms.
Why Shopify Stands Out
- Automatic updates ensure your store is always protected against the latest threats.
- PCI-DSS compliance helps secure payment processing without extra effort.
- Strict app security reduces the risk of vulnerabilities from third-party tools.
- DDoS protection prevents cyberattacks that could take your store offline.
If security is a top concern, choosing a Shopify store against emerging cyber threats is a proactive step in protecting your business. In the final section, we will discuss how to stay ahead of cyber risks and future-proof your store.
Lock Down Your Store with Confidence.
Your Shopify store’s security should never be an afterthought. At OyeCommerz, we help you implement advanced Shopify services that protect your business and customer data, while optimizing for performance. Whether you’re just launching or scaling rapidly, our custom solutions ensure you’re always one step ahead of emerging threats.
Let’s future-proof your Shopify store, securely and smartly.
Contact to Migrate your Site to Shopify Now
Conclusion
Securing your Shopify store in 2025 isn’t just about installing a plugin, it’s about proactive, layered defense strategies. While Shopify’s native security features, like SSL encryption and fraud protection, offer a strong foundation, true resilience comes from combining platform tools with smart practices: regular audits, strong authentication, and real-time threat monitoring.
Emerging cyber threats will only grow more deceptive, but so too will the technologies defending against them. Store owners who take action now will not only protect their digital storefronts but also build lasting trust with their customers.
Integrating Shopify services for security today means safeguarding revenue tomorrow. Review your store’s vulnerabilities, adopt the right tools, and fortify your eCommerce future, starting now.
Frequently Asked Questions
Use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, install trusted security apps, update your themes/apps regularly, and monitor user permissions.
Implement firewalls, SSL encryption, AI-based threat detection, data backups, and educate your team on phishing and fraud.
Yes, Shopify provides built-in security including PCI DSS compliance, SSL certificates, fraud analysis, and secure payment processing.
Shopify uses 256-bit SSL, regular platform updates, PCI-compliant hosting, and AI-powered fraud detection systems.
Shopify is generally secure, but merchants must actively manage app permissions, use strong credentials, and stay vigilant against phishing or third-party vulnerabilities.


